In-Depth Guide to Hyperscale Computing in 2024
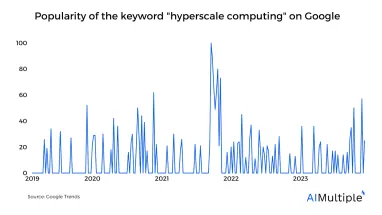
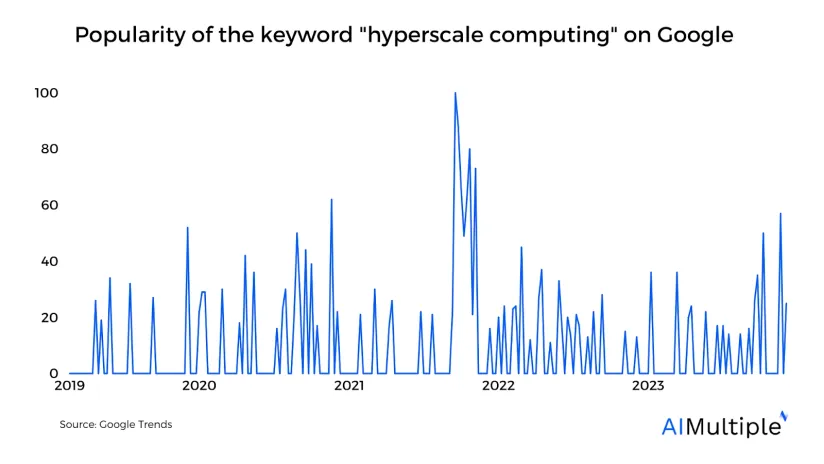
Figure 1. Popularity of the keyword “hyperscale computing” on Google worldwide
To accommodate the growing demand for AI-driven services, hyperscale data centers are on track to triple their infrastructure capacity by 2028, building upon their existing global footprint of ~1000 major data centers as of mid-2023.1 This article explains what hyperscalers are, their benefits, frequently asked questions (FAQ) on hyperscale computing, and the top hyperscale cloud service providers.
What is hyperscale cloud computing?
Hyperscale refers to a cloud service provider that delivers a wide array of scalable resources, including computing power through virtual machines, storage, and networking capabilities, across vast, globally distributed data centers. These providers leverage advanced automation and massive infrastructure investments to support extensive computing needs, allowing businesses to swiftly scale up or down based on demand. Hyperscalers play a critical role in facilitating digital transformation, offering the agility and capacity necessary for enterprises to innovate and adapt in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Top 6 hyperscale cloud providers
In the year 2022, AWS, Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) collectively generated an estimated revenue of ~$170 billion, dominating ~50% of the hyperscale market.2 Here, we list the top companies providing hyperscalers:
1- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
2- Microsoft Azure
3- AliBaba Cloud
4- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
5- IBM Cloud
6- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
These providers are recognized for their extensive global infrastructure, innovative services, and the ability to support vast computing resources on demand.
Hyperscale computing architecture

Source: EdgeCore3
Figure 2. Simplified layout of a hyperscale data center
Here is a breakdown of the key components of hyperscalers and their functions:
- Local Area Network (LAN): The LAN is critical for internal communications within the data center. It connects all the components, such as servers, storage, and networking equipment, allowing them to communicate and transfer data at high speeds.
- Internet connection: Hyperscale data centers are typically operated by companies that provide services over the Internet. Therefore, robust connectivity to the internet is crucial for delivering services to users globally.
- Spine: In a spine-leaf architecture, the spine is the backbone of the data center network. It provides a high-capacity, centralized routing system that ensures all leaf switches can communicate with each other and with external networks.
- Leaf: Leaf switches provide direct network connections to servers and storage systems. They form the access layer of the data center network and are crucial for distributing the network traffic efficiently.
- IPMI Switch: Hyperscale data centers have thousands of servers, and managing them efficiently is vital. The IPMI switch allows remote management of servers for tasks like monitoring, updating, and troubleshooting, which is essential for maintaining the health and performance of the data center.
- Servers: Servers are the workhorses of any data center, performing computational tasks and running the applications that provide services to end-users.
- Storage: Hyperscale data centers deal with vast amounts of data. Efficient storage systems are necessary to store, retrieve, and manage data at scale. The storage edge is important for delivering content rapidly to users by positioning data geographically closer to them or caching frequently accessed data.
The benefits of hyperscale data centers
1. Ease of infrastructure management
Hyperscale data centers offer an unparalleled level of management over the foundational components of IT infrastructure: physical space, servers, storage systems, and network connectivity. This holistic approach ensures that businesses can rely on highly efficient, secure, and scalable environments for their computing needs. By centralizing the oversight of these critical areas, hyperscale data centers alleviate the burdens traditionally associated with IT infrastructure management, allowing companies to focus more on their core operations and less on the complexities of maintaining their digital frameworks.
2. Efficient power distribution
By dividing electrical power into smaller, manageable packets, these facilities can achieve a higher level of energy efficiency and reliability. This method allows for more precise control over power allocation, ensuring that each component receives the exact amount of energy it requires, no more, no less. This reduces waste and minimizes the risk of overloads and power-related failures. Furthermore, packet-based power distribution can adapt to dynamic workloads, scaling up or down as demand fluctuates, in line with the major aim of hyperscale computing.
3. Cost-effective
Hyperscaler providers propose a long-term commitment model through “reserved instances,” where businesses can secure cloud resources for an extended period. This approach grants discounts of up to 70%, depending on the commitment’s duration.4 By agreeing to use specific resources or services for a set minimum period, companies can achieve significant cost savings compared to usage-based billing.
4. Efficient cooling and energy consumption
Hyperscale data centers excel in their approach to cooling and energy consumption, setting them apart as models of efficiency. These facilities are designed from the ground up to optimize airflow and utilize advanced cooling technologies, such as liquid cooling and outside air cooling, to manage the immense heat generated by high-density computing equipment. By doing so, they significantly reduce the energy required to maintain optimal operating temperatures, leading to a lower overall energy footprint.
5. High computing power
The hallmark of hyperscale data centers is their immense computing power, capable of supporting the most demanding applications and workloads. These facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art servers that feature the latest in processing, memory, and storage technologies. The high computing power is essential for handling big data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and complex simulations at scale. Hyperscale data centers can process and analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, providing businesses with the insights they need to make informed decisions quickly.
6. Complex responsibility is outsourced to the hyperscale provider
Hyperscaler providers significantly simplify IT infrastructure management for businesses by assuming responsibility for the bulk of the technical workload. This approach allows companies to offload tasks such as maintaining data center infrastructure, securing servers, managing storage, and ensuring network connectivity. As a result, businesses can dedicate more resources to strategic areas like operating system configuration, database management, and application security.
Here is a table on the responsibilities shared between hyperscale providers and customers:
Table 1. Components of hyperscalers and assigned reponsible parts.
| Component | Topic | Responsible |
|---|---|---|
| Data center infrastructure | Infrastructure of the data center (including physical access controls) | Hyperscaler |
| Server | Server infrastructure and security of physical servers | Hyperscaler |
| Storage | Storage infrastructure including RAID components, connection between server and storage,
and redundancy
| Hyperscaler |
| Network | Physical components and cabling of all physical network components (including
servers and storage)
| Hyperscaler |
| Backbones | Connectivity between the data centers as well as the regions
(e.g., Frankfurt to London) using the backbone network of the hyperscalers
| Hyperscaler |
| Operating system | Setup, configuration, and security of the operating system | Customer |
| HANA database | Setup, configuration, user and access management, etc. | Customer |
| SAP application | Operation and management of the technical SAP components (SAP Central
Services, application server, etc.)
| Customer |
| SAP data and programs | Data residing in the SAP system and ABAP/Java programs | Customer |
| SAP access | User, passwords, roles, and profiles | Customer |
| Firewalls and network | All virtual components of the cloud environment | Customer |
| Encryption | Any encryption of the network traffic, storage, backup, or any
other configuration
| Customer |
Source: Apress5
> FAQ on hyperscale computing
1- What are the differences between enterprise data centers and hyperscale data centers?
The main differences between enterprise data centers and hyperscale data centers lie in their scale, architecture, and operational focus:
- Scale: Hyperscale data centers are significantly larger, often sprawling over millions of square feet to accommodate the extensive infrastructure required to support vast amounts of computing resources and storage capacities. Enterprise data centers, while still sizable, are typically smaller and cater to the specific needs of a single organization.
- Architecture: Hyperscale data centers employ highly automated, standardized, and optimized architectures designed for large-scale operations, emphasizing efficiency and scalability. Enterprise data centers may adopt a more customized approach to meet the particular IT and business requirements of the organization.
- Operational Focus: Hyperscale data centers are built to serve a wide range of customers and applications, from cloud computing services to big data analytics, requiring them to prioritize flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Enterprise data centers often focus on specific organizational needs, prioritizing security, compliance, and integration with existing IT infrastructure.
2- Are hyperscalers better than cloud services?
Hyperscalers are, in fact, a subset of cloud service providers, distinguished by their vast scale, global reach, and comprehensive service offerings. The question of whether hyperscalers are “better” than other cloud services depends on the specific needs and scale of the business. Hyperscalers offer unparalleled scalability, a wide array of services, and significant cost efficiencies, making them an excellent choice for large enterprises and applications with global reach. However, smaller cloud providers may offer advantages such as specialized services, greater flexibility, or closer customer support.
3- What is the difference between high-performance computing (HPC) and hyperscale computing?
High Performance Computing (HPC) focuses on delivering high computational power to solve complex scientific, engineering, or data analysis problems, often using parallel processing techniques.
Hyperscale computing, on the other hand, emphasizes scalability, elasticity, and efficiency to support large-scale internet services, data analytics, and cloud computing workloads. While HPC targets raw computational speed for specific tasks, hyperscale computing is about managing large-scale infrastructure efficiently.
4- What are the factors to consider when deciding if hyperscale is right for my business operations?
When evaluating hyperscale infrastructure for your business, consider the following:
- Big Data Analytics Requirements: If your operations involve analyzing large datasets to derive insights, hyperscale computing can provide the necessary resources.
- Cloud Computing Specific Projects: Projects that demand scalable, flexible cloud resources are well-suited to hyperscale environments.
- Digital Transformation Goals: If your organization aims to modernize its IT infrastructure and services, hyperscalers can offer the tools and platforms to support this transformation.
- Focus on Scalability: Businesses needing to scale resources quickly to meet demand will benefit from the elastic nature of hyperscale computing.
If you need assistance, don’t hesitate to contact us:
External Links
- 1. “Hyperscale data-center capacity on pace to triple over next six years.“October 27, 2023. Network World. Retrieved February 20,2024.
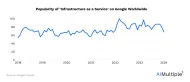
- 2. “Worldwide infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) hyperscaler market share from 2020 to 2023, by vendor.” Statista. February 2024. Retrieved February 20, 2024.
- 3. “Hyperscale Data Center.” Edge-core. Retrieved February 20, 2024.
- 4. “Bögelsack, A., Chakraborty, U., Kumar, D., Rank, J., Tischbierek, J., & Wolz, E. (2022). Introduction to Public Cloud and Hyperscalers.” In SAP S/4HANA Systems in Hyperscaler Clouds: Deploying SAP S/4HANA in AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure (pp. 1-27). Berkeley, CA: Apress. Retrieved February 20, 2024.
- 5. “Bögelsack, A., Chakraborty, U., Kumar, D., Rank, J., Tischbierek, J., & Wolz, E. (2022). Introduction to Public Cloud and Hyperscalers.” In SAP S/4HANA Systems in Hyperscaler Clouds: Deploying SAP S/4HANA in AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure (pp. 1-27). Berkeley, CA: Apress. Retrieved February 20, 2024.

Cem is the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per Similarweb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
Sources:
AIMultiple.com Traffic Analytics, Ranking & Audience, Similarweb.
Why Microsoft, IBM, and Google Are Ramping up Efforts on AI Ethics, Business Insider.
Microsoft invests $1 billion in OpenAI to pursue artificial intelligence that’s smarter than we are, Washington Post.
Data management barriers to AI success, Deloitte.
Empowering AI Leadership: AI C-Suite Toolkit, World Economic Forum.
Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU, European Commission.
Public-sector digitization: The trillion-dollar challenge, McKinsey & Company.
Hypatos gets $11.8M for a deep learning approach to document processing, TechCrunch.
We got an exclusive look at the pitch deck AI startup Hypatos used to raise $11 million, Business Insider.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.