In-depth Guide to Invoice Automation in 2024
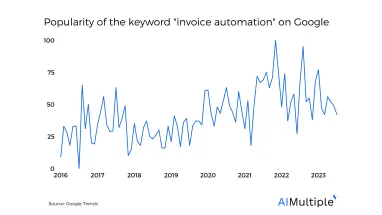
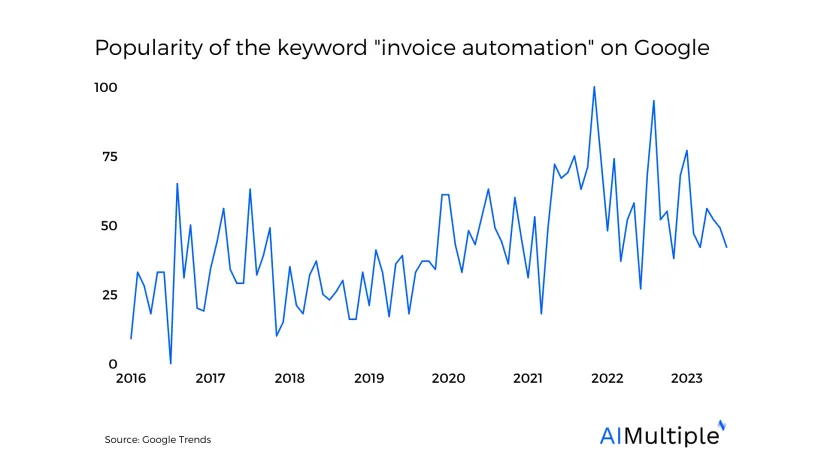
Invoice automation (also called automated invoice processing) is a maturing area of automation within accounts payable (AP) / procure-to-pay (P2P) automation with limited implementation risks and significant benefits. Invoice automation would free up back office finance/procurement teams to focus on higher value added tasks. Therefore, it is not surprising to see its popularity increase.
However, invoice automation process is more complex than most executives are aware of. This knowledge gap creates challenges in understand the value of invoice automation and slows down its adoption. We will outline major components of invoice automation and highlight best practices.
What is invoice automation?
To understand invoice automation, it makes sense to understand what an invoice is and the different types of invoices from an automation perspective. Invoice automation is a critical part of a company’s accounts payable management which is part of the procure-to-pay (p2p) process (also called source-to-pay s2p).
Invoice automation can achieve straight through processing (STP) (i.e. automation with no human interaction) most of the time for the entire invoice process.
How does it work?
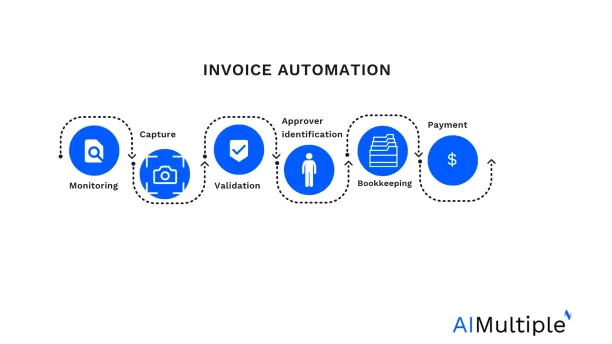
Invoice automation (Figure 1) involves
- Monitoring for invoices: Invoices can arrive via various channels. Different invoices from different channels need to be processed differently:
- Invoice exchange platforms:
- Your firm’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) platform
- Buyer-supplier e-invoicing networks
- PDF files with attached e-invoice formats can be shared via email or centralized portals as mandated by the local authorities
- Email: PDF or other image formats can be used to share invoices via email. An RPA bot or a simple email automation tool can flag emails with invoices and forward them for data extraction. Most companies use one or more dedicated email address for invoices to further simplify invoice monitoring.
- Mail: For hard-copy invoices, companies tend to use a single address to centralize invoice scanning.
- Invoice exchange platforms:
- Invoice capture: Extracting relevant details (e.g. bank account, ordered item) from the invoice. If software does not have confidence in the results, it is sent to employees for a manual check. The format of the document is important for capture accuracy
- Invoices may be shared in structured data format (e.g. JSON or XML) via invoice exchange platforms or PDF files with attached metadata. These can be perfectly extracted.
- Invoices in these formats need to be extracted using OCR and machine learning:
- images or PDF documents in emails.
- scan images from invoices sent by post.
- Invoice validation: Evaluating invoice against order records and other criteria to ensure that the payment is indeed a valid one.
- Approver identification: Personnel or software solutions need to identify the right personnel to approve the document. Once approver is identified, the invoice can get approved either automatically using established policies or manually by the approver.
- Bookkeeping: Recording invoice-related information in systems. For this, invoices without purchase orders need to be added to a general ledger account and machine learning solutions can be used to match invoices to accounts.
- Payment: Using working capital optimization policies to decide payment time and to make the necessary payment to settle the invoice
How does manual invoice processing work?
Before automation, back-office teams would
- Check email and post for invoices
- Examine invoices, understand the relevant data in the invoice
- Feed invoice data to the relevant systems so payments and system records would be complete
- In rare cases, team would notice irregularities in the invoice and contact the supplier or the ordering team to resolve the issues.
What are the benefits of invoice automation?
Increased compliance
A digital and automated invoice process is likely to reduce fraud since it:
- Leaves an audit trail, creating transparency
- Performs automated checks. For example, bank account changes can be highlighted to prevent invoice fraud.
Early payment discounts
Companies leveraging automated invoice processing can take advantage of more early payment discounts if their cashflow allows it. This is because:
- Automation reduces invoice processing time.
- Machine learning powered invoice capture solutions can automatically extract invoice payment terms, highlighting potential early payment discounts.
Reduction of manual errors
Elimination of manual data entry: Through use of invoice automation software capabilities like OCR (Optical Character Recognition) or IDP (Intelligent Document Processing), enterprises can automate manual data entry. Removing this repetitive work for simple invoices enables employees to focus better, make fewer mistakes and focus on higher value tasks.
Efficiency
As with any automation process, an automated invoice process has the potential to significantly increase the number of invoices processed per employee. Businesses can cut their costs by $13 each invoice. The annual savings for a business processing a few thousand invoices each month can be almost half a million $/year.1
Improved financial visibility
Invoice automation can provide real-time visibility into the accounts payable process, enabling better cash management. The accounts payable department can see where an invoice is in the approval process and when it’s due, which helps with predicting cash flow and identifying potential bottlenecks. For example, if an invoice is stuck in the approval process, the team can quickly intervene to ensure the invoice is processed in a timely manner. This can contribute to a better accounts payable workflow.
What is the current level of invoice automation?
Almost all PO invoices submitted through a company’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) are automatically processed. Automation challenges exist for other invoices:
- non-EDI PO invoices: For large companies a significant share of invoices (up to 50%) are sent by smaller companies that are not part of the company’s EDI. Issues in PO number identification are preventing a sizable percentage of these from automated processing
- non-EDI non-PO invoices: Most Fortune 500 companies are currently using outdated technology leveraging OCR and rules-based programming to process these documents. As a result, they are able to rarely achieve end-to-end automation while leading edge, deep learning based AP AI platforms can process most invoices in a completely automated manner. Further automation challenges within this category include:
- handwritten invoices
- invoices with unexpected information (e.g. change of bank account information)
How can enterprises increase invoice automation rates?
Though enterprises face similar challenges to SMEs, the scale of the challenge is different since a globally diverse supplier base shares a more heterogeneous set of invoices. New technological advancements in this domain include the use of large language models including GPT models in accounting.
Why is invoice automation important?
Since the whole invoice management process is already digital, we have seen companies deprioritize invoice processing automation. This would be a mistake because a manual digital process is almost as expensive as a manual analog process. In a digital but manual process, invoices, the invoices, their metadata and payments are digital but the process is no less time consuming than a completely analogue process.
This issue of manual labor in digital processes is a widespread issue as companies initially focused on digitizing processes but not automating them. With the rise of RPA, processes like invoice automation were automated. Our collection of RPA case studies revealed that invoice automation was one of the most common areas of RPA automation. However, RPA is not a customized solution for invoice processing and can end up achieving lower levels of automation compared to solutions specialized in invoice processing.
What are the leading invoice automation companies?
There are 2 main types of invoice automation solutions:
1- Specialized software
- Accounts payable management solutions provide specialized invoice automation solutions mainly for SMEs and mid-market companies.
- AP AI is an emerging category that aims to provide an end-to-end automation solution for enterprises.
For some of AP automation tools we analyzed check:
- Dynamics 365 in Accounts Payable Automation: In-Depth Review
- NetSuite Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in 2024
- Blackbaud Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in ’24: In-Depth Review
- Sage Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in ’24
- 7 Vic.AI Alternatives to Automate Accounting in 2023
- Top 10 ReadSoft Alternatives / Competitors
- Top 10 Kofax Alternatives/Competitors in 2023
- 14 Rossum AI Competitors/Alternatives in 2023
2- Generalist software which can be used in invoice automation
- RPA tools can be used to automate invoice processing. However, RPA is a process-agnostic solution and therefore
- buyers would need to customize it for their invoice process
- the solution would lack some enterprise invoice automation functionality like identifying the cost centers of non-PO invoices.
- Process mining software can help businesses identify issues in their accounts payable process and build rules-based automation solutions to address bottlenecks.
If you have questions, feel free to contact us:
External Links
- 1. “How Much Does It Really Cost to Process an Invoice?”. Quadient. Retrieved December 28, 2022.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow onNext to Read
5 Benefits of Balance Sheet Reconciliation Automation in 2024
Accounts Payable Automation in 2024: 7 Steps & 45+ Solutions
Good points on why automation is important. Are you familiar with human in the loop automation? I’ve been looking a lot of places and have found other software that include this feature (bisok is one). Do you know if Kofax does something similar? My department is looking at several solutions. Thank you for your help
Hi Matthias, thank you for contributing.
Most ML based invoice automation vendors (e.g. Hypatos and others) offer human-in-the-loop (HITL) functionality to enable continuous learning. Kofax allows users to modify templates which I wouldn’t call human-in-the-loop functionality since template configuration is not as simple as HITL. In HITL, you improve future extraction results just by clicking on fields on the document, which is what ML based vendors offer. However, in Kofax, you need to improve an existing template which requires a lot of thinking and ultimately results in a solution that is not robust, suppliers often change templates or churn.
And heads up, had to remove the link in your comment as per our policy. If we allow links, we get too many low value comments.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.