Meter Data Management System in '24: 10+ tools & applications
Utility companies stand to gain significant advantages by embracing meter data management, a key strategy for efficiently managing and interpreting meter data. Leveraging meter data for customer service metrics not only minimizes customer turnover but can also boost company profits by more than 20% through the implementation of accurate pricing strategies.
Despite these compelling benefits, only 28% of utility providers have actively integrated digital technologies, such as Meter Data Management (MDM) systems, to harness the potential of big data, automation, and predictive analytics.
This low adoption rate may be attributed to a lack of knowledge in the utility automation field and the complexity of the available tools and landscape.
We provide a concise guide to support utility providers in navigating the complexities of meter data management. This resource covers use cases, benefits, and highlights top tools, empowering professionals to make informed decisions for optimized operations and maximized benefits.
What is meter data management?
Meter Data Management (MDM) refers to a crucial component within utility systems that collects, store, and process data generated by various meters. MDM systems manage and streamline the vast amounts of information produced by utility meters, such as those measuring electricity, gas, or water consumption.
How does meter data management work?
Meter Data Management (MDM) systems play a crucial role in handling the intricate processes associated with metering in modern utility systems. The ways MDM systems operate include:
- Providing meter data central (MDC) system: The Meter Data Central system serves as a centralized repository for raw data collected from smart meters. It acts as a hub for initial data processing, validating and storing information before it is further analyzed or utilized by downstream systems.
- Managing meter data flows: These meters are equipped with advanced communication capabilities, allowing them to collect and transmit detailed consumption data in real-time. MDM systems interact with smart meters to capture the data they generate.
- Collecting and aggregating data: The process begins with smart meters collecting consumption data at frequent intervals, such as every 15 minutes. The meter data flows from these smart meters to the Meter Data Management system. The MDM system aggregates and consolidates this data from various meters across the utility network.
- Validating and editing data: Meter Data Management systems perform rigorous validation checks on the incoming data. This involves verifying the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of the data. Any discrepancies or errors detected during this stage are corrected to ensure the reliability of the information.
- Enabling storage and retrieval: Once validated, the meter data is securely stored in the MDM system’s centralized repository. This stored data can be retrieved for various purposes, such as billing, analysis, or compliance reporting. The historical data records stored in the MDM system offer a comprehensive view of consumption patterns over time.
- Analyzing data and reporting activities: Meter Data Management systems provide utilities with the capability to analyze the collected data. By leveraging advanced analytics, utilities can gain insights into consumer behavior, identify trends, and optimize their operations. The MDM system facilitates the generation of detailed reports that aid in decision-making and planning.
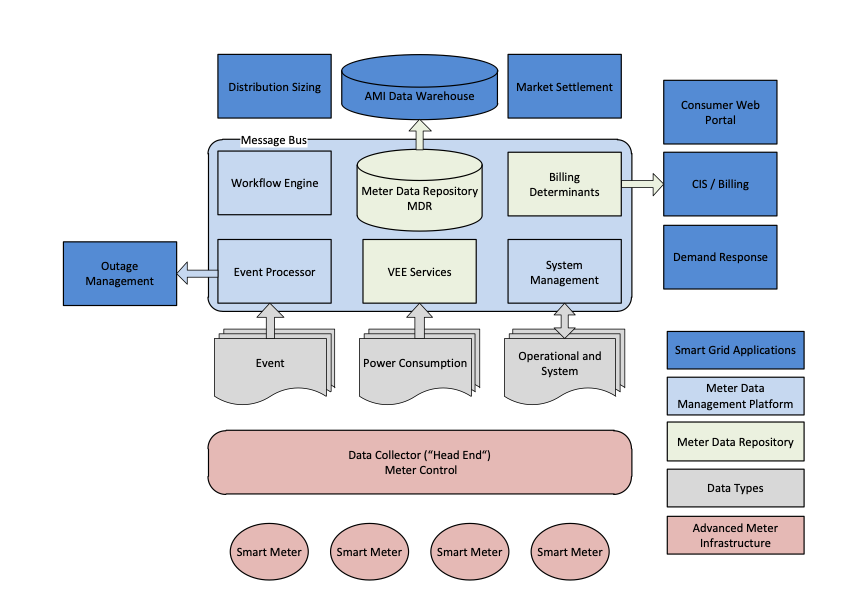
Advanced metering infrastructure and advanced MDM
Advanced MDM tools integrate with advanced metering infrastructure and smart meter infrastructure to manage meter data flows, ensure data accuracy, and enable insightful analysis. Advanced metering infrastructure is an integrated system that connects MDM with couple of tools along with smart grids, such as:
Smart Meters and data concentrators: Smart meters deployed in homes and businesses, forming a part of the smart grid. Smart meters replace traditional utility meters, offering advanced functionalities such as real-time data collection and two-way communication. Data concentrators act as intermediaries, aggregating and relaying information between smart meters and the central systems.
Wide-area communication network (WAN): The Wide-area communication network enables seamless communication and data transfer across a widespread geographical area. This network facilitates the exchange of information between smart meters, data concentrators, and the central systems, ensuring a robust and interconnected infrastructure.
Home Area Network (HAN): The Home area network is an integral part of AMI that extends the connectivity of smart meters to the consumer’s premises. It enables communication between smart meters and in-home devices, allowing consumers to monitor and manage their energy consumption in real time.
Top meter data management systems and tools
Various vendors provide MDM tools. The table below lists some of these MDM tools with its respective B2B review numbers and scores gathered from Gartner, providing a clear overview of user feedback and performance evaluations.
| MDM tools | B2B Reviews |
|---|---|
| SAP Cloud for Energy | 4.3/5.0 based on 42 reviews |
| PI System by SE | 4.3/5.0 based on 37 reviews |
| Utilities Meter Data Management by Oracle | 4.5/5.0 based on 29 reviews |
| Fluentgrid MDMS | 4.5/5.0 based on 19 reviews |
| EnergyIP Meter Data Management by Siemens | 4.4/5.0 based on 16 reviews |
| Smart Grid Suite (ASGS) by Atos | 4.6/5.0 based on 14 reviews |
| Itron Enterprise Edition Meter Data Management | 3.8/5.0 based on 10 reviews |
| Gridstream Meter Data Management System by Landis+Gyr | 4.4/5.0 based on 6 reviews |
| Connexo by Honeywell | 4.4/5.0 based on 4 reviews |
| Sensus by Xylem | 4.0/5.0 based on 1 reviews |
| Utilihive by Greenbird | 4.0/5.0 based on 1 reviews |
Other utility systems to integrate
MDM can be integrated with other utility systems which can enable automated meter reading, improved management reports.
Workload automation tools: WLA is a scalable solution that can run across multiple systems to manage and automate the scheduling and execution of various tasks and processes, including those related to data processing and analytics. Integration with MDM ensures optimized data processing workflows and efficient utilization of computing resources. Explore top WLA vendors in our constantly updated lists and data-driven and objective WLA tools benchmark.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA): SCADA systems monitor and control the physical processes in the utility network. Integration with MDM allows for a more comprehensive view of system operations, aiding in data validation and contextual analysis.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS systems provide spatial data management. Integrating GIS with MDM allows utilities to visualize meter locations, analyze consumption patterns in geographic context, and enhance outage management.
Customer Information System (CIS): CIS systems manage customer data, billing, and service information. Integration with MDM ensures accurate billing based on real-time consumption data and facilitates better customer service.
Outage Management System (OMS): OMS systems detect, respond to, and manage power outages. MDM can analyze historical consumption data to identify outage patterns and anomalies. This analysis might reveal trends associated with specific outage causes, helping utilities enhance their outage response and prevention strategies.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): ERP systems like SAP manage various business processes. Integration with MDM supports streamlined financial processes, data reconciliation, and overall business intelligence. Discover SAP utility solutions in our objective and data-driven benchmarking and SAP meter-to-cash technologies.
MDM use cases
Meter Data Management (MDM) systems offer a range of use cases that significantly benefit utility companies. Here are some key applications:
Data management for smart meter data
MDM systems help utility companies to efficiently manage the vast amounts of data generated by smart meters, ensuring accurate collection, validation, and storage of consumption data.
Asset management
MDM systems contribute to effective asset management by providing utilities with insights into the health and performance of their metering infrastructure. This aids in identifying and addressing issues promptly, optimizing asset lifecycle, and reducing maintenance costs.
Load and demand forecasting
Leveraging historical consumption data stored in the MDM system, utility companies can conduct sophisticated load and demand forecasting. This helps in anticipating peak usage periods, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing overall grid reliability.
For example, Pepco used special technology (AMI and MDMS) to track how much energy 5,400 transformers were using every hour. 1 This helped them find cases where the transformers were working too hard. When customers used less energy during busy times, Pepco gave them discounts on their bills. This effort saved 4 million kWh of energy and gave customers $5 million in bill discounts each summer.
Consumption data analysis
MDM systems enable utilities to analyze consumption data in-depth, gaining insights into consumer behavior and patterns. This information is valuable for tailoring services, implementing demand-side management strategies, and optimizing energy distribution.
Enhanced transparency for billing
Utility companies use MDM systems to seamlessly integrate meter data into their billing systems. This ensures accurate and timely billing based on actual consumption patterns, enhancing transparency and customer satisfaction.
Ensured efficient data flow
MDM systems facilitate communication across wide area communication network system by connecting with smart meters dispersed across a utility’s service area. This ensures the efficient flow of data between meters and the central MDM system, supporting real-time monitoring and control.
MDM benefits
Here is a list of Meter Data Management (MDM) benefits using the specified keywords:
- Improved energy efficiency: MDM systems contribute to enhanced energy efficiency by providing utilities with detailed insights into consumption patterns. This information enables utilities to identify areas of inefficiency and implement targeted strategies to optimize energy usage.
- Reduced energy waste: By analyzing data collected from smart meters, MDM systems help utilities identify and mitigate instances of energy waste. This proactive approach supports sustainable practices and reduces unnecessary energy consumption.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: MDM systems play a pivotal role in improving customer service metrics by ensuring accurate billing based on real-time consumption data. This transparency enhances customer trust and satisfaction with utility services.
- Also, MDM helps consumers save money by delivering insights into their usage patterns. This information enables consumers to make informed decisions about energy conservation, leading to potential cost savings on utility bills.
- Ensured long-term data storage: MDM systems provide utilities with the capability for long-term data storage. This historical data archive supports trend analysis, load forecasting, and future planning, allowing utilities to make informed decisions based on comprehensive datasets.
Further reading
Discover more on utility automation by discovering top tools and technologies:
- Compare 10 SAP Utility Solutions based on +3000 reviews
- Compare 10 Smart Meter Solutions based on 500+ reviews
- Improved Meter-to-Cash Process with 10 Tips & 9 Solutions
External sources
- 1. “Identifying Transformer Overload & Enabling Demand Response.” Itron. Accessed at January 29, 2024.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.