Invoice Parsing to Automate Invoice Processing in 2024

Source: Docsumo
Manual invoice processing is a time-consuming and error-prone task. It requires a significant amount of effort and resources to extract data from invoices and enter it into accounting systems. Since invoice processing is a critical component of any business, many businesses have turned to invoice parsers to automate the process.
Invoice parsing is an innovative technology that automates data extraction from invoices. It reduces the manual and time-consuming task of data entry, allowing businesses to focus on more important tasks. Implementing invoice parsing tools can greatly improve a company’s efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. To help business leaders leverage the technology this article discusses how invoice parsing works, the benefits of implementing this technology, and tips for successfully implementing invoice parsers.
What is invoice parsing?
Invoice parsing uses automated tools such as NLP, NLU, OCR, and other data extraction technologies to automatically extract data from invoices in various formats, such as PDFs, images, etc.
An invoice parser is a software program that extracts information such as
- Vendor name
- Invoice number
- Amount due
and inputs it in a machine-readable format. This data can be utilized for multiple functions, such as automating accounts payable, completing month-end accounting closures, and managing invoices.
The parser software is usually integrated into an invoice processing system, which automates the entire process from the receipt of an invoice to payment.
How does invoice parsing work?
Documents written in a certain markup language are read and handled by parsers. They break the document up into smaller pieces, called tokens, and then look at each token to figure out what it means and where it fits in the structure of the whole document.
To do this, parsers need to know a lot about the grammar of the markup language in question. This gives them the ability to recognize each token and figure out the exact connections between them.
The process is comprised of 5 steps:
1. Input
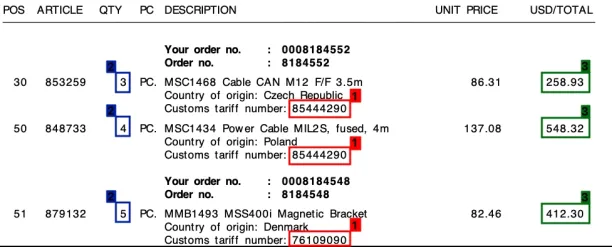
Figure 2. Sample invoice input Source: Stack Overflow
Invoices can be received in a variety of formats, including paper, email, or electronic formats such as PDF or XML. The invoice parser software will typically accept these invoices as input.
2. Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
If the invoice is in a scanned paper or image format, the parser will use OCR technology to extract text from the image. This allows the parser to access the data contained within the invoice.
Some invoice parser solutions use AI-powered OCR technology that can automatically extract information from PDFs, photos, and scanned data without the need for new rules or templates. This is because the AI can handle semi-structured and unfamiliar documents and improve over time. The extracted information can be customized to only include specific tables or data entries.
3. Data extraction
The parser will then extract specific information from the invoice, such as the vendor name, invoice number, date, and item details. This is typically achieved using a combination of pattern recognition and machine learning algorithms.
Some invoice parsing software has the capability to extract key information such as the invoice date, number, tax identification numbers, and various totals by using predefined filters:
Some parser tools offer the ability to extract line item information from invoices with a consistent format by creating a separate document parser for each specific vendor or trading partner layout:
4. Data validation
Once the data has been extracted, the parser will validate the information to ensure that it is accurate and complete. This can include checking that the date is in the correct format, that the vendor name matches a predefined list of vendors, or that the item details match the expected format.
5. Data output

Figure 3. Sample invoice output Source: Stack Overflow
The extracted and validated data is then outputted in a format that can be easily imported into the user’s accounting or ERP system. This can be in the form of a CSV file, database record, or directly into an accounting software.
Challenges with manual invoice data extraction
Manually extracting data from invoices and entering it into a system can be challenging for companies as there are several complexities:
Human Error
Invoices can contain a large amount of data, and manual entry increases the risk of errors, such as typos, transposition of numbers, and incorrect data entry. Inaccuracies in data entry are responsible for an estimated $600 billion in yearly losses.1
Time-Consuming
On average, it takes 17 days, or approximately 75% of a month, to manually process a single invoice.2
Many different pieces of important information are included in invoices, and they are all presented in a key-value style where an individual identification serves as both the key and the value. The process of manually extracting these pairs is time-consuming and involves many inspections to assure accuracy. Even some OCR algorithms struggle to detect extracted values without context.
Lack of Standardization
Invoices from different suppliers may have different formats. Each invoice is generated with a unique format that can pose difficulties when processing and interpreting these patterns. The documents, such as emails, paper, and PDFs, may go through a lot of digital and paper records before being approved for payment, making manual extraction of data challenging and prone to error.
Inefficient Process
The manual handling of invoices, which incurs an average cost of almost $23 per invoice3, can be both time-consuming and expensive, leading to an inefficient and repetitive process.
Potential for Data Loss
There is a risk of losing data if invoices are lost or damaged or if data is not entered correctly into the system.
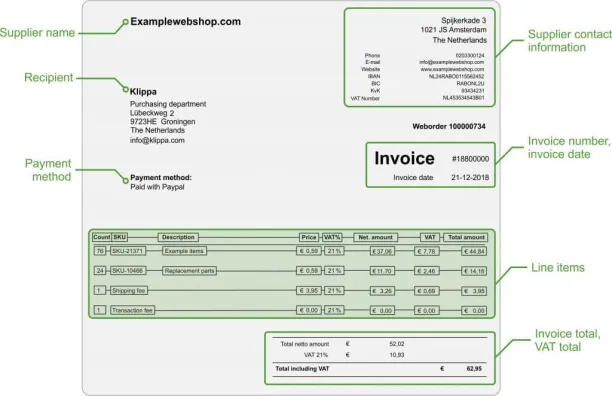
Figure 4. OCR of invoice lines Source: Klippa
OCR systems often face difficulties in extracting line items from invoices as well. This is because transaction tables may lack horizontal or vertical lines, making it difficult for OCR to establish context for the extracted items.
For more on invoice process automation
To explore different technologies that your business can leverage for AP automation, read our in-depth articles:
- Accounts Payable (AP) Automation Tools Benchmarking in 2023
- Accrual Automation: How To Improve Accrual Workflow in 2023
- Automated Invoice Validation: Benefits & Use Cases in 2023
- 20 AP Automation Case Studies: Analysis of Benefits & Use Cases
- General Ledger Software in 2023: Benefits and Key Features
- 4 Steps to Automated Payment Reconciliation in 2023
For some of AP automation tools with invoice automation capabilities, also check:
- Dynamics 365 in Accounts Payable Automation: In-Depth Review
- NetSuite Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in 2024
- Blackbaud Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in ’24: In-Depth Review
- Sage Accounts Payable (AP) Automation in ’24
- 7 Vic.AI Alternatives to Automate Accounting in 2023
- Top 10 ReadSoft Alternatives / Competitors
- Top 10 Kofax Alternatives/Competitors in 2023
- 14 Rossum AI Competitors/Alternatives in 2023
If you have any additional queries regarding invoice parsing tools and best practices, do not hesitate to get in touch with us:
This article was drafted by former AIMultiple industry analyst Kübra İpek.
External Links
- 1. “Simple Mistakes Can Cost Big Money; Is Your Business at Risk?”. Itemize. Retrieved 6 February, 2023.
- 2. “AP automation or Accounts Payable automation software News”. PRWire. Retrieved 1 February, 2023.
- 3. “AP automation or Accounts Payable automation software News”. PRWire. Retrieved 1 February, 2023.

Cem is the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per Similarweb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
Sources:
AIMultiple.com Traffic Analytics, Ranking & Audience, Similarweb.
Why Microsoft, IBM, and Google Are Ramping up Efforts on AI Ethics, Business Insider.
Microsoft invests $1 billion in OpenAI to pursue artificial intelligence that’s smarter than we are, Washington Post.
Data management barriers to AI success, Deloitte.
Empowering AI Leadership: AI C-Suite Toolkit, World Economic Forum.
Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU, European Commission.
Public-sector digitization: The trillion-dollar challenge, McKinsey & Company.
Hypatos gets $11.8M for a deep learning approach to document processing, TechCrunch.
We got an exclusive look at the pitch deck AI startup Hypatos used to raise $11 million, Business Insider.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.