5 Smart Process Mining Steps to Achieve Better Results in '24
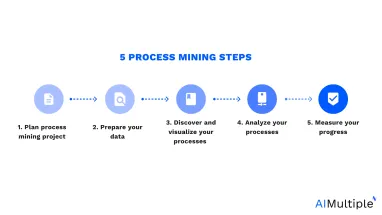
Process mining is a modern way to achieve process improvement and management, which is why 93% of business leaders aim to deploy it. Yet, 79% of the same leaders have never used the tool for any process. 52% of the leaders claim that the low rates of adoption is related to the lack of process mining expertise. An antidote is understanding process mining steps.
Therefore, in this article, we’ll explain the 5 main process mining steps that business leaders should learn if they want to stop postponing process mining deployment across their organizations.
1. Plan process mining project
Before starting deploying process mining solutions, executives should decide on the parties that will be in-charge of the project.
Executives should create a team composed of process analysts, data scientists and IT team members, so that they can all collaborate in each step.
For instance, a data science team would guide process analysts through the data preparation phase, whilst the process analysts themselves are tending to process analysis.
Creating such a large team requires good coordination so that the project does not take longer than it should. Therefore, it is better to plan the process mining project journey and define each organ’s responsibility ahead of time.
2. Prepare your data
The second process mining step is the data wrangling which contains gathering, cleaning and transforming data. Process mining stats show that 80% of the efforts and time is spent on the data preparation step.
Process mining utilizes event logs data which primarily consists of case ID, timestamps and event information (See Figure 1).
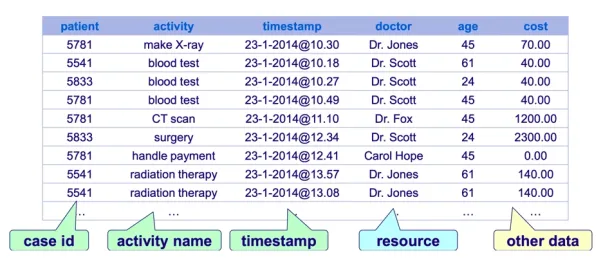
In some cases, additional data might be required. For example, a company wants to adopt process mining for detecting maverick buying. In such use cases, they need details such as the vendor name, invoice number, discount and payment date.
Typically, most companies:
- Extract their data from ERP systems
- Transform them into various tables
- And store them in data warehouses for reporting and analytics purposes
For the process mining data preparation phase, analysts are expected to address if the quantity and quality of the data stored in the warehouse is good enough or not.
3. Discover and visualize your processes
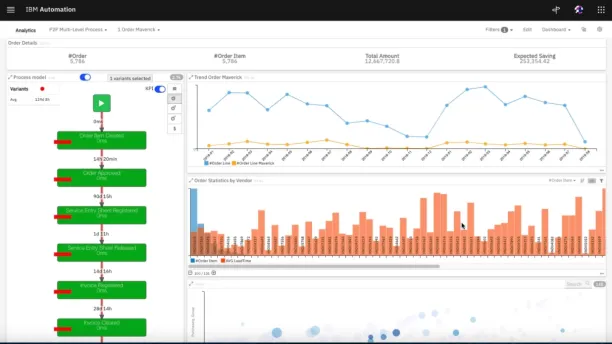
In this phase, process mining algorithms leverage the data to automatically discover processes and visualize them.
Process mining tool gathers all the tasks, activities and transactions as one interactive process map. In this dynamic map, analysts can zoom out and view the entire process workflow with all complexity and dive into each path that cases follow.
As a result, analysts can easily identify the deviating paths or investigate their happy paths to set them as the best practices.
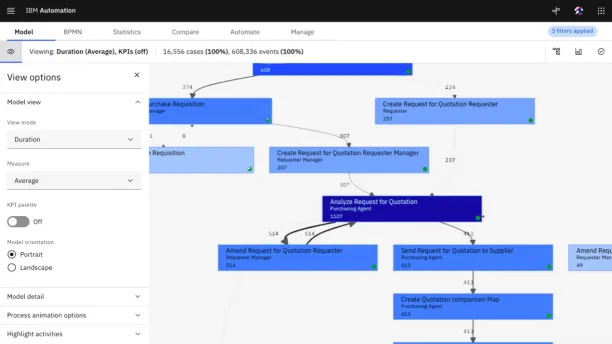
4. Analyze your processes
At this stage, process mining software allows users to run process analysis and measure process performance.
Process mining offers standard dashboards and analysis for the business processes, enabling process excellence teams to obtain insights. These insights provide answers to generic KPIs, such as cost and time management.
Many tools allow users to customize the dashboards and reports. Analysts can evaluate process performance by setting the required KPI. They can filter and drill down into the analytics to verify if their hypotheses are correct or not.
For such evaluation, analysts check out whether process steps are:
- Prolonging to complete
- Skipping steps or activities (overlooking to vital details or failing to complete an activity)
- Including unplanned activities
- Deviating from the target model
- Containing overlapping or duplicating activities
- Escalating and slow downing processes
If the processes suffer from any of these problems, analysts should start digging into root-causes behind these bottlenecks. Traditionally, process analysts are expected to raise questions to locate the bottleneck and the reason why it occurs.
However, leading process mining vendors include automated root cause analysis on their platforms to associate issues with potential reasons.
It can be related to heavy workload on employees, high dependency over manual-work or lack of standardization across process execution, requiring process automation and other process improvement efforts.
5. Measure your progress
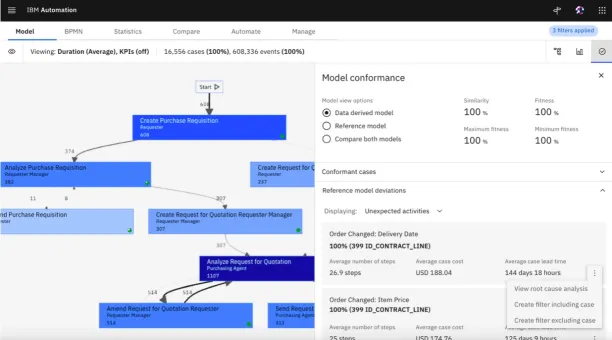
Conformance checks, one of the three main process mining components, ensure that analysts understand the difference between as-is and as-if processes.
Conformance checks compare the real processes against the reference model users upload and deliver the percentages of conforming cases to this ideal model. This way, process analysts can pinpoint deviations and better implement best practices.
Conformance checks also help analysts to measure their progress once they start implementing changes to improve process bottlenecks. Measuring the progress with conformance checks is data-driven and accurate.
On the other hand, it is still valuable to take qualitative measures into account. Therefore, process excellence teams should share their findings with the parties in-charge of executing the process to receive feedback, specific questions and critiques. Their opinion will allow the team to go back to the tool and re-analyze.
What is process mining?
Process mining extracts event log data from information systems like enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) to generate insights into business operations. By creating visual process models and graphs, it enables organizations to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and reduce operational costs through a data-driven approach.
People often confuse process mining and data mining due to both involving data analysis, yet the distinction lies in focus. Process mining centers on optimizing business processes through event logs, while data mining is a broader concept for extracting patterns and knowledge from diverse datasets.
What are process mining benefits?
Process mining tools help business analysts compare key performance indicators, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes by employing end-to-end visualization and process analytics. This data-driven approach leads to reduced cost, improved efficiency and continuous process optimization.
How does process mining work?
Process mining leverages machine learning to analyze process data from information and IT systems. By creating actual process models, it enables organizations to understand, improve, and automate processes. This approach helps identify bottlenecks, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance, supporting a proactive data-driven strategy for end-to-end process visibility and optimization.
Further reading
Explore advices and best practices to apply process mining, business process management and improvement:
- 6 Steps to Successfully Choose a Process Mining Vendor
- How to Implement Process Improvement in 6 Steps?
- 5 Best Practices for Processes Management in 2022
Compare all process mining tools by using our data-driven and comprehensive process mining vendor list.
Check out comprehensive and constantly updated list of process mining case studies to learn process mining steps and apply them better through real-life examples.
And, if you need more help in identifying the right vendor for you, let us know:
Sources

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.